It’s important to know how to add new users to WordPress. Whether you’re running a multi-author blog, managing a business website, or operating an online store, the ability to add and manage users is crucial. By adding new users, you can delegate responsibilities, streamline workflow, and ensure that someone with the appropriate skills and permissions handles each aspect of your website. For instance, authors can be given the ability to write and edit posts without accessing more sensitive areas of the site, such as theme and plugin settings.
Moreover, adding new users is not just about delegation and division of labor; it’s also about security and efficiency. By assigning specific roles and capabilities to different users, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized changes to your site and reduce the likelihood of errors.
Step-by-Step Guide to Adding a New WordPress User
- Go to your WordPress admin page and log in to your website. If you’re not sure of your password, you can click “Lost Password” to reset it. There’s more detailed instructions for resetting your WordPress password here.
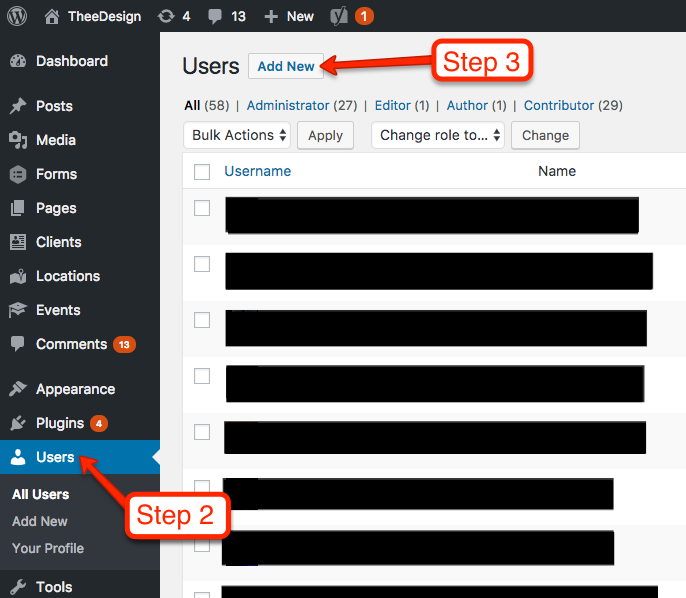
- Now that you’re in the WordPress dashboard, click on Users in the left sidebar.
- Towards the top of the screen, click Add New.

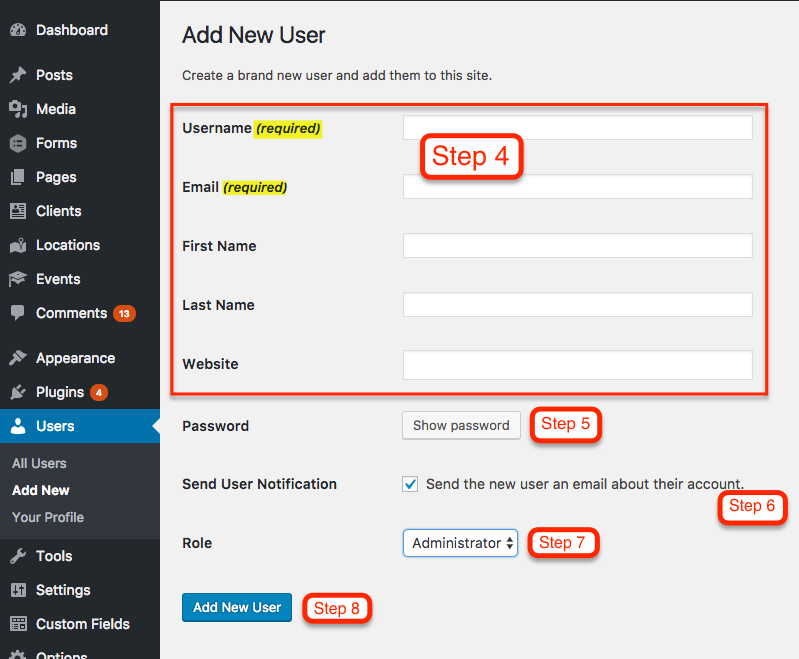
- Now you should be on the Add New User screen. Enter a username and email address for your new user. First name, last name, and website are optional.
- Enter a SECURE password for your new user. You can either use the one that WordPress randomly generates, or create your own. However, it’s important to use a secure password because hackers will try to use your login to compromise your website. Please choose a password with uppercase, lowercase, numbers and symbols.
- Keep the Send User Notification checked if you would like the new user to receive an email with their login information.
- Choose a Role for your new user. Administrator is the default and it gives the user access to all the features of the website. If you need to limit the permissions of your new user, see the other roles available below.
- Click the Add New User button and you’re all set!

Understanding WordPress User Roles
WordPress is designed with a comprehensive role-based access system that defines what each user can and cannot do on your website. Understanding these user roles and their associated permissions is crucial for effective website management. There are five primary user roles in WordPress: Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber. Each role is equipped with specific capabilities, allowing for a granular level of access control.
- Administrator: This role is at the top of the WordPress user hierarchy. Administrators have complete control over the website, which includes the ability to add and remove users, change user roles, access all posts, pages, comments, themes, plugins, and settings. Essentially, an Administrator has the power to make any changes to the site. This role is typically reserved for site owners and should be granted sparingly to prevent security risks.
- Editor: Editors have extensive control over the content sections of the website. They can add, edit, publish, and delete any posts and pages, including those written by others. This role also allows them to moderate comments, manage categories, tags, and links. Editors do not have access to change site settings, themes, or plugins, making this role ideal for those who manage content but do not need full site control.
- Author: Authors can write, edit, publish, and delete their own posts, but they cannot access or modify content created by others. They can also upload files and images. This role is well-suited for regular content creators who do not require oversight of other contributors’ work.
- Contributor: Contributors can write and edit their own posts but cannot publish them. Instead, their posts must be reviewed and published by an Editor or Administrator. Contributors cannot upload files or images. This role is perfect for guest writers or lower-level content creators who need editorial oversight.
- Subscriber: The Subscriber role has the most limited capabilities. Subscribers can only manage their own profiles and read content on the website. They cannot write posts, view comments, or access any administrative features. This role is typically used for visitors who sign up to receive updates or access member-only content.
Each of these roles is designed to offer a specific level of access, ensuring that users can perform their tasks without interfering with areas outside their purview. By assigning the appropriate roles to your team members, you can maintain a well-organized and secure WordPress environment. Understanding and utilizing these roles effectively is key to managing a successful WordPress site.
Simply choose the desired user role in the drop down on the Add New User screen. (see Step 7)
Advanced User Addition Techniques
While the standard method of adding users one by one in WordPress is straightforward, there are scenarios where more advanced techniques are required. Two such scenarios are bulk user addition and adding users without email addresses. These techniques can save time and accommodate unique user management situations.
Bulk User Addition
- Understanding Bulk User Addition: In cases where you need to add a large number of users to your WordPress site, adding them individually can be time-consuming. Bulk user addition is a process that allows you to add multiple users at once, significantly streamlining the process.
- How to Implement: To add users in bulk, you typically need to use a plugin designed for this purpose. Plugins like ‘Import Users from CSV‘ allow you to create a CSV (Comma-Separated Values) file with user details such as usernames, email addresses, roles, and more. Once you have prepared your CSV file, the plugin will enable you to upload it and automatically create user accounts for each entry in the file. This method is particularly useful for educational institutions, membership sites, or any large-scale WordPress project.
Adding Users Without Email Addresses
- Why Add Users Without Email Addresses: There might be situations where you need to create user accounts without email addresses. This could be due to privacy concerns, internal network restrictions, or when setting up accounts for users who will not interact with the site directly.
- Methodology: WordPress, by default, requires an email address for each user. To bypass this, you can use a plugin that allows user registration without an email address. These plugins typically provide an alternative way of identifying users, such as using a unique username. It’s important to note that while this method can be useful in certain contexts, it also bypasses some of the built-in security features of WordPress, such as email verification and password reset options. Therefore, it should be used judiciously and with a clear understanding of the potential security implications.
Both bulk user addition and adding users without email addresses are advanced techniques that can make user management more efficient in specific scenarios. However, it’s crucial to use these methods with an understanding of their implications, especially in terms of site security and user management. Always ensure that any plugins used for these purposes are reliable, well-maintained, and compatible with your version of WordPress.
Managing User Permissions and Roles
Effectively managing user permissions and roles is a critical aspect of maintaining the security and efficiency of a WordPress site. As your website evolves, you may need to change user roles and permissions to reflect the changing responsibilities and access levels of your team members. Here’s how you can manage these aspects effectively:
How to Change User Roles
- Accessing User Profiles: To change a user’s role, first navigate to the ‘Users’ section in your WordPress dashboard. Here, you will see a list of all the users registered on your site.
- Editing User Roles: Locate the user whose role you want to change and click on their username to access their profile. Scroll down to the ‘Role’ dropdown menu in the profile. This menu lists all the available roles – Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber.
- Selecting a New Role: Choose the new role you wish to assign to the user. Be mindful of the permissions associated with each role to ensure you are granting the appropriate level of access.
- Saving Changes: After selecting the new role, scroll to the bottom of the page and click the ‘Update User’ button. This action will save the changes and update the user’s role.
Best Practices for User Role Management
- Assign Roles Judiciously: Always assign the lowest level of access necessary for a user to perform their tasks. This principle, known as the principle of least privilege, helps in minimizing potential security risks.
- Regularly Review User Access: Periodically review the roles and access levels of all users, especially after a project is completed or when a team member’s role changes. Remove or downgrade access for users who no longer need it.
- Use Custom Roles and Capabilities: For more granular control, consider using plugins that allow you to create custom user roles and define specific capabilities. This is particularly useful for large teams or websites with specialized needs.
- Educate Users About Their Roles: Ensure that users understand the scope of their roles and the responsibilities that come with them. This understanding helps prevent misuse of privileges and maintains the integrity of your site.
- Keep User Information Up to Date: Encourage users to keep their profiles, especially their email addresses, up to date. This ensures that they receive necessary notifications and can reset their passwords if needed.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively manage user roles and permissions on your WordPress site. Proper management not only enhances security but also ensures that each team member has the access they need to be productive and efficient.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When managing a WordPress site, particularly in the context of adding and managing users, certain common mistakes can occur. These errors can range from minor inconveniences to significant security vulnerabilities. Understanding these mistakes and knowing how to avoid them is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient website.
Typical Errors During User Addition
- Assigning Incorrect Roles: One of the most frequent mistakes is assigning inappropriate roles to users. This can lead to users having either too much or too little access to your site. To avoid this, always double-check the role you are assigning and ensure it aligns with the user’s needs and responsibilities.
- Overlooking Username and Email Verification: Sometimes, in haste, administrators might not verify usernames and email addresses properly. This can lead to issues like duplicate accounts or users not receiving important notifications. Always verify the details entered and ensure that each user has a unique username and a valid email address.
- Neglecting to Remove Inactive Users: Failing to remove or downgrade users who no longer need access to your site can pose a security risk. Regularly audit your user list and remove or change the roles of users who no longer need access.
Security Considerations
- Using Weak Passwords: Allowing users to set weak passwords can make your site vulnerable to attacks. Enforce strong password policies and encourage users to use passwords that are a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Not Updating User Permissions: As roles and responsibilities change, so should user permissions. Failing to update these can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive areas of your site. Regularly review and update user permissions as needed.
- Ignoring User Role Customization: Relying solely on default user roles can sometimes grant more permissions than necessary. Consider using plugins to create custom roles tailored to the specific needs of your site.
- Lack of Monitoring and Auditing: Not monitoring user activities and auditing roles regularly can lead to unnoticed security breaches or misuse of user privileges. Implement auditing and monitoring tools to keep track of user activities.
- Disregarding Two-Factor Authentication: Not using two-factor authentication (2FA) is a missed opportunity to enhance security. Encourage or enforce the use of 2FA for all users to add an extra layer of security to your site.
By being aware of these common mistakes and implementing the suggested precautions, you can significantly improve the user management and security of your WordPress site. Remember, proactive management and regular audits are key to maintaining a secure and well-functioning website.
FAQs
When managing users in WordPress, several questions often arise, especially regarding the addition and modification of user roles. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions and their answers to help you navigate these aspects more effectively.
Can I Add Multiple Users at Once in WordPress?
Yes, you can add multiple users at once in WordPress, but this functionality is not available by default. To do this, you will need to use a plugin that allows bulk user uploads, typically through a CSV (Comma-Separated Values) file. These plugins enable you to upload a file containing the details of multiple users, including their usernames, email addresses, and roles, thereby streamlining the process of adding a large number of users simultaneously.
How Do I Change a User’s Role in WordPress?
To change a user’s role in WordPress, navigate to the ‘Users’ section in your WordPress dashboard. Click on the username of the user whose role you want to change to access their profile. Scroll down to the ‘Role’ dropdown menu and select the new role you wish to assign to the user. Remember to click the ‘Update User’ button at the bottom of the page to save your changes.
Is It Safe to Give Someone an Administrator Role?
Giving someone an Administrator role in WordPress should be done with caution. The Administrator role has complete control over the site, including the ability to add and remove users, change user roles, and modify core site settings. This role should typically be reserved for site owners or trusted individuals who need full access to the site. Always ensure that the person you are assigning the Administrator role to is trustworthy and understands the responsibilities that come with it.
What Happens If I Add a User with an Incorrect Email Address?
If you add a user with an incorrect email address, they will not receive any notifications from WordPress, including the initial email to set their password. This means they won’t be able to log in to your site. To rectify this, you will need to edit the user’s profile and update the email address to the correct one.
Can Users Change Their Own Roles in WordPress?
No, users cannot change their own roles in WordPress. Role management is an administrative task, and only users with sufficient permissions, such as Administrators, can change user roles. Users can edit their profiles to change their personal information, like their email address or password, but they cannot alter their role within the site.